A sample text widget
Etiam pulvinar consectetur dolor sed malesuada. Ut convallis
euismod dolor nec pretium. Nunc ut tristique massa.
Nam sodales mi vitae dolor ullamcorper et vulputate enim accumsan.
Morbi orci magna, tincidunt vitae molestie nec, molestie at mi. Nulla nulla lorem,
suscipit in posuere in, interdum non magna.
|
There’s been much press coverage of the travails of the AmLaw 100 — America’s largest law firms. Clients are aggressively pushing back against ever-increasing hourly rates and significant inefficiencies. Storied firms have been folding, merging and laying off staff and even attorneys at unprecedented levels. Electronic discovery specialists and legal outsourcing are compressing margins for the litigation work that historically fueled big firm profits. Non-traditional legal providers are hardly faring better. Clearspire, a much-heralded pioneer of the virtual law firm concept, closed shop in June.
Yet at the same time — and perhaps as a consequence — the market for legal startups is booming. VentureBeat commented that the profession’s ongoing transition is “fueling innovation throughout the entire industry.” In 2009, just 15 legal services startups were listed on AngelList. There are now more than 400 startups and almost 1,000 investors. A whopping $458 million was invested into legal startups last year, a remarkable increase from the $66 million that went into the space in 2012. Legal entrepreneurs are focused on two different objectives: helping lawyers do their work better, faster and cheaper, and making the law more accessible, sometimes eliminating the need for lawyers altogether.

It is the second, consumer-facing portion of this trend that portends a fundamental change in the legal market. By giving both individual and corporate consumers the resources to do it yourself, today’s crop of disruptive legal startups is laying the groundwork for an era in which software tools, social sharing and document comparison-assembly programs are positioned to replace attorneys’ stock in trade, namely reuse of contracts and other legal “forms.”
A century ago the bar protected itself with arcane Latin phrases and obscure judicial reporters. Two decades ago, it used the expense of private legal research databases like LexisNexis, an information barrier that is increasingly archaic in today’s era of Web-enabled courts and Google Scholar. With the present challenge to the largest traditional domain of legal practice — creation, revision and execution of legally binding documents — technology is breaking down walls that made have legal U.S. services unaffordable, and thus essentially unavailable, to many except the wealthy those at the opposite end of the economic spectrum who qualify for free and pro bono legal services.
Continue reading Legal Disruptions Redux
There’s a famous old political adage — “where you stand is where sit” (also known as Miles’ Law) — meaning basically that government policy positions are dictated more by agency imperative and institutional memory than objective consideration of the public interest. A related concept is “regulatory capture,” where administrative agencies over time become defenders of the status quo and pursue objectives more for regulated firms as their constituency than consumers. Capture theory is closely related to the “rent-seeking” and “political failure” theories developed by the public choice school of economics. Or as Harold Demsetz put it well in his influential 1968 article, Why Regulate Utilities?, “in utility industries, regulation has often been sought because of the inconvenience of competition.”
That’s no longer limited to electricity companies and other public utilities these days. With the advent of rapid, low-cost entry into previously sheltered markets, powered by technology and the sharing economy, today’s incumbent industries are taking regulatory capture and politics as rent seeking to new heights. At DisCo we’ve written extensively about Uber, Lyft, Airbnb, Tesla and many other disruptive new start-ups that are facing a backlash from established industries (taxis, hotels and auto dealers, respectively) which use consumer protection as a Trojan Horse to disguise preventing or delaying competition on price, features and service. Politicians in locales as diverse as New York, New Jersey, San Antonio and Seattle (believe it or not!) have, wittingly it seems, gone along so far.

This is where what antitrust lawyers dub competition advocacy comes into play. Most antitrust policy in the U.S. is made in federal court as a result of merger, monopolization and horizontal collusion prosecutions launched by the Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). But due to our federal-state system and a judge-made doctrine allowing states to exempt some markets from competition despite federal antitrust demands (government action, and private conduct to obtain such action, is challengeable in only relative narrow circumstances), much of the battle takes place in the legislative and regulatory arenas. Accordingly, competition advocacy is the primary tool available to antitrust enforcers in the U.S. to oppose state and local regulations favoring established firms over start-ups and parochially sheltering in-state companies from out-of-state competitors. The result is that for three decades the federal antitrust agencies have engaged in affirmative outreach to state and local legislators and regulators in the form of comments, letters and occasional lawsuits that seek to drive home the basic truths that competition outperforms regulation and the law should not pick winners and losers when it comes to evolving markets. (State attorneys general also undertake competition advocacy, principally through amicus briefs, as well.)
Continue reading Competition Advocacy Matters—Here’s Why and How
Three high-level staffers at the Federal Trade Commission (Andy Gavil, Debbie Feinstein and Marty Gaynorare) are backing Tesla Motors Inc. in its ongoing fight to sell electric cars directly to consumers. As we’ve observed, Tesla forgoes traditional auto dealers in favor of its own retail showrooms. But that business model was recently banned by the New Jersey Motor Vehicle Commission — and is under fire in many other states as well — as a measure supposedly to protect consumers.
 The ubiquitous state laws in question were originally put into place to prevent big automakers from establishing distribution monopolies that crowd out dealerships, which tend to be locally owned and family run. They were intended to promote market competition, in other words. But the FTC officials say they worry (as have we at DisCo) that the laws have instead become protectionist, walling off new innovation. “FTC staff have commented on similar efforts to bar new rivals and new business models in industries as varied as wine sales, taxis, and health care,” the officials write in their post. “How manufacturers choose to supply their products and services to consumers is just as much a function of competition as what they sell — and competition ultimately provides the best protections for consumers and the best chances for new businesses to develop and succeed. Our point has not been that new methods of sale are necessarily superior to the traditional methods — just that the determination should be made through the competitive process.” The ubiquitous state laws in question were originally put into place to prevent big automakers from establishing distribution monopolies that crowd out dealerships, which tend to be locally owned and family run. They were intended to promote market competition, in other words. But the FTC officials say they worry (as have we at DisCo) that the laws have instead become protectionist, walling off new innovation. “FTC staff have commented on similar efforts to bar new rivals and new business models in industries as varied as wine sales, taxis, and health care,” the officials write in their post. “How manufacturers choose to supply their products and services to consumers is just as much a function of competition as what they sell — and competition ultimately provides the best protections for consumers and the best chances for new businesses to develop and succeed. Our point has not been that new methods of sale are necessarily superior to the traditional methods — just that the determination should be made through the competitive process.”
As Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk noted earlier this year, “the auto dealer franchise laws were originally put in place for a just cause and are now being twisted to an unjust purpose.” Yes, indeed. It is pure rent seeking by obsolescent firms. State and local regulators have eliminated the direct purchasing option by taking steps to shelter existing middlemen from new competition. That’s not at all consumer protection, it is instead economic protectionism for a politically powerful constituency. Thanks to the FTC staff, some brave state legislators may now be emboldened to resist the temptation to decide how consumers should be permitted to buy cars.
Unfortunately, the issue is not limited to automobiles. I wrote recently about how in New York City, officials want to ban Airbnb because its apartment rental sharing service is not in compliance with hotel safety (and taxation) rules. The New York Times last Wednesday editorialized in support of that approach, arguing that Airbnb is reducing the supply of apartments and increasing rents. They’re wrong, of course, because short-term visits obviously do not substitute for years-long apartment leases. But the more important issue is that one economic problem does not justify reducing competition in a separate market. If New York actually has an apartment rent price problem, banning competition for hotels is no more a solution than prohibiting direct-to-consumer auto sales.
Originally prepared for and reposted with permission of the Disruptive Competition Project.

Every new year sees a slew of top 5 and top 10 lists looking backwards. Here’s one that looks forward, predicting the five biggest disruptive technologies and threatened industries for 2014.
Making projections like these is really hard. Brilliant pundit Larry Downes titles his new book (co-authored with Paul Nunes) Big Bang Disruption: Strategy In an Age of Devastating Innovation. Its thesis is that with the advent of digital technology, entire product lines — indeed whole markets — can be rapidly obliterated as customers defect en masse and flock to a product that is better, cheaper, quicker, smaller, more personalized and convenient all at once.
Since adoption is increasingly all-at-once or never, saturation is reached much sooner in the life of a successful new product. So even those who launch these “Big Bang Disruptors” — new products and services that enter the market better and cheaper than established products seemingly overnight — need to prepare to scale down just as quickly as they scaled up, ready with their next disruptor (or to exit the market and take their assets to another industry).
Disruptors can come out of nowhere and happen so quickly and on such a large scale that it is hard to predict or defend against. “Sustainable advantage” is a concept alien to today’s technology markets. The reputation of the enterprise, aggregated customer bases, low-cost supply chains, access to capital and the like — all things that once gave an edge to incumbents — largely no longer exist or are equally available to far smaller upstarts. That’s extremely unsettling for business leaders because their function is no longer managing the present but inventing the future…all the time.
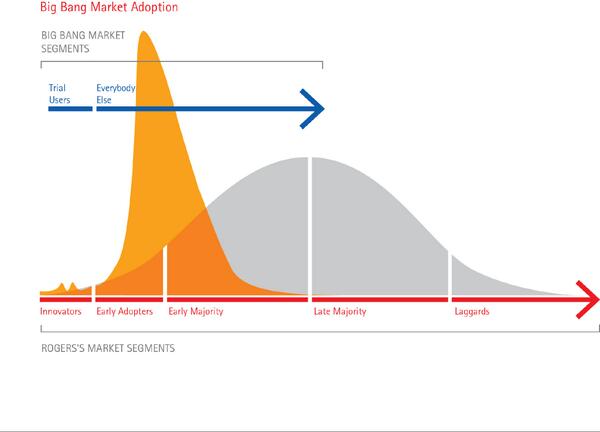
I certainly have no crystal ball. Yet just as makers of stand-alone vehicle GPS navigation devices were overwhelmed in 2013, suddenly and seemingly out of nowhere, by smartphone maps-app software, e.g., Google Maps, etc., so too do these iconic industries and services face a very real and immediate threat of big bang disruption this year.
Continue reading 5 Industries Facing Disruption In 2014
Despite the failures in recent years of such well-known retail chains as Circuit City, Borders and the like, it is way too soon to declare that the Internet will replace brick-and-mortar retailing. In part that is because consumer research suggests that in some segments, such as clothing, feeling and touching merchandise is an important part of the buying experience. Of interest to students of technological disruption, retailers are beginning in earnest to deploy technologies marrying the best aspects of online retailing with shopping malls and physical stores.
Delivery is one area where online retailers remain at a disadvantage. Amazon counters with its Prime membership for free two-day delivery, Amazon Lockers for local pick-up and its experimental foray into drone deliveries. Startups like Deliv (described as “a crowdsourced same-day delivery service for large national multichannel retailers”) are now providing equivalently fast store or home delivery for both online and in-person purchases.
Four of the nation’s largest mall operators are turning their properties into mini-distribution centers for rapid delivery, meaning shoppers can ditch their bags and keep spending. The service promises set delivery times for purchases consumers make at the mall or online from mall tenants, facilitated by a Silicon Valley start-up, Deliv Inc….The move highlights how delivery has become a key battleground in the war between physical and online retailers.
Startup Offers Same-Day Delivery at Shopping Malls | WSJ.com.

That in itself is remarkable. It shows that disruption is not a one-way street for legacy retailers. Yes, theirs is a challenging business environment, but technology is beginning to supply features for physical stores that meet and in some cases can beat online shopping providers. Home Depot, for instance, offers a smartphone app that allows consumers to check store inventory and aisle location, scan QR and UPC codes to get more information about products and order online with in-store delivery, overcoming some of the chain’s long-standing weaknesses: confusing layouts, out-of-stock merchandise and resulting abandoned visits.
Perhaps the most controversial realm is that of in-store consumer tracking and special offer distribution. This made news just last week when Apple Inc. turned on its iOS7 “iBeacon” service at its own retail stores. Macy’s has activated a shopkick-powered service through which simply walking into a Macy’s location will automatically send specialized offers to customers depending on where they are in the store. As Wired observed:
That’s just the beginning, though. Retailers are already talking about things like in-store navigation and dynamic pricing, all made possible by beacon-enhanced retail locations. For independent shops, iBeacon is a chance to jump into the smartphone era with one fell swoop. A $100 beacon is all it takes for even the mustiest book store to track customers, make recommendations, and offer discounts to customers’ pockets.
The risk, however, is that consumers may reject secret tracking technologies that retailers use internally, absent notice and consent. Over the last two years, retailers such as Nordstrom have hired software firms that gather Wi-Fi and Bluetooth signals emitted from smartphones to monitor shoppers’ movements around stores. They use the data to study things like wait times at the check-out line and how many people who browse actually make a purchase. At the prompting of Sen. Charles Schumer (D-NY) and the Washington, DC-based advocacy group Future of Privacy Forum, several location-tracking firms agreed in October to a code of conduct under which they will ask retailers to post signs in “conspicuous” spots in stores which inform consumers that their movements are being monitored and direct them to a website where they can opt-out. As Kashmir Hill noted in Forbes:
As with many novel and unexpected uses of technology, people have tended to be creeped out by the practice when they learn about it. Ask Path, which was tracking shoppers in malls (in 2011). Or Nordstrom, which came under fire earlier this year for tracking its shoppers without clear notice. Or London, which was using trash bins to collect info from passerbys’ mobile devices.
The flip side is that by offering recommendations and deals with an opt-in policy, retailers could dramatically bridge the divide between the online and brick-and-mortar experiences, making the latter still more like the former. Few consumers react negatively to Amazon or Netflix offering recommended products based on their past purchases. By doing the same thing in real-time, when a shopper passes the relevant store aisle or section, physical retailers would be in a position to offer something no e-commerce site can match: customized shopping with the ability to see, feel and take home impulse purchases enabled by technology.
There remain a slew of legal questions about whether the data collected by location-technology providers and retailers qualifies as personally identifiable data subject to the European Union Privacy Directive and the corresponding EU Safe Harbor in the U.S. In this country, it seems likely that the unique phone IDs associated with wireless devices — which are only linked to subscribers in the carrier’s switching and billing systems — would not be considered personal data by the Federal Trade Commission. In Europe, countries like the Netherlands and France have already articulated a more expansive view which could encompass device information in addition to name, address, phone numbers and the like. But even in the more liberal America, some have questioned whether retailers will be forced, whether by consumers or regulators, to dial-back autonomous tracking and adopt more transparent location practices.
All of this brings back memories for me personally. Nearly 15 years ago, I represented a start-up that was developing GPS chips for smartphones. While they are now ubiquitous (the start-up was sold to Qualcomm in March 2000), the challenges in making GPS work without a dedicated, external antenna were substantial. So like any good disruptor, my client went to the Federal Communications Commission to advocate cell phone location rules for E911 service that could give it a competitive advantage in the marketplace. The anecdote we used in our lobbying was that McDonald’s could message your phone, when passing one of its outlets, asking “Have you had your break today?” (That certainly dates the message, of course).
Technology has evolved so much that shopping is now almost at that place. Location tracking platform providers and their retail clients are offering a degree of interactivity never before available at retail. Whether it is compelling or creepy to consumers, of course, remains to be determined.
Note: The author has represented shopkick Inc., but not in connection with the company’s privacy policies and practices. Originally prepared for and reposted with permission of the Disruptive Competition Project.

As a recent story from the The Washington Post illustrates well, “tradition” is a gating factor in the ongoing transformation of the legal industry. Despite the highly conservative nature of courts, bar associations and attorneys, however, in the post-Great Recession legal market of 2013, technology and changing values are rapidly disrupting traditional legal services.
My colleague and friend Jonathan Askin, Founder of the Brooklyn Law Incubator & Policy Clinic, hosted a seminar on legal start-ups in late August. Many of the companies highlighted there are focused on low-hanging fruit, taking the trend started by LegalZoom of moving do-it-yourself work product to consumers into spaces that for decades have remained buttoned-up by prohibitions against “unauthorized practice of law” and the resistance of lawyers to allowing clients document control. (LegalZoom itself has been challenged by bar groups and class action plaintiffs in North Carolina, Connecticut, Missouri and California for allegedly engaging in the practice of law, a classic and anticompetitive use of regulations designed to protect consumers, not prohibit new business models.) Like taxi-hailing companies Uber and Sidecar, legal start-ups thus face opposition from incumbents who are well-situated to employ archaic regulatory regimes to thwart new entry.
Nonetheless, the four emerging firms Askin profiled make a persuasive case that the guild-like barriers which for centuries protected lawyers from competition are breaking down before our eyes.
- Shake allows consumers to create binding contracts automatically on their smartphones or tablets with a few Q&As and then sign them electronically.
- Lawdingo leverages the power of networking to connect consumers to lawyers for real-time quick (and often free) answers on a virtually unlimited number of topics.
- Caserails offers cloud-based document assembly and editing functionalities for individuals or groups, long the bane of corporate transactions.
- Priori Legal allows SMBs to select among a trusted community of lawyers for discounted or fixed-rate engagements with Web-based comparison shopping.
The best and brightest of these firms will undoubtedly rise to the top over time. Much like banks in the 1970s — when toasters as deposit “gifts” were replaced by deregulated interest rates and tellers by ATMs — legal consumers no longer care or very much appreciate the old traditions of the legal profession, especially its convoluted language, fancy office space and expensive artwork. The successful start-ups in this steady disintermediation of legal services will be the ones who recognize that they are driven by what legal transactions can and will be, not what they have been historically, and that they are technology companies solving legal problems, not legal companies trying to understand technology. Continue reading Disrupting the Legal Industry
The U.S. economy has seen its share of disruptive technologies derailed (at least in time-to-market) by archaic legal regimes. Look to Uber’s taxi-hailing service and Airbnb’s apartment rental innovations as recent examples. Most times it’s a case of old assumptions about consumer protection and competition having lost validity with changed circumstances. Other times it’s simple protectionism by legacy incumbents, as in the legal assault on Aereo’s IPTV streaming service for alleged copyright infringement. In the case of electric auto developer Telsa Motors, however, it’s something a little different.
 The problem for Tesla’s well-reviewed vehicles — Consumer Reports gave the new Tesla S its highest car rating ever — is not technical, as the California start-up boasts impressive lithium battery innovations and is aggressively building its own chain of recharging stations. Instead the constraint is a plethora of state laws (48 in all) that prohibit or limit automobile manufacturers from selling direct to consumers or owning auto dealerships. These statutes, which date to the 1950s, are matched by a federal law known as the “Automobile Dealers’ Day In Court Act.” That legislation is an anomaly which allows dealers (franchisees) to sue in their home federal district court and recover legal fees if a manufacturer fails to “act in good faith in performing or complying with any of the terms or provisions of the franchise, or in terminating, canceling or not renewing the franchise with said dealer.” (These sorts of lawsuits would otherwise require a minimum of $75,000 at stake, would be governed by state law and would not have the threat of fee-shifting.) The problem for Tesla’s well-reviewed vehicles — Consumer Reports gave the new Tesla S its highest car rating ever — is not technical, as the California start-up boasts impressive lithium battery innovations and is aggressively building its own chain of recharging stations. Instead the constraint is a plethora of state laws (48 in all) that prohibit or limit automobile manufacturers from selling direct to consumers or owning auto dealerships. These statutes, which date to the 1950s, are matched by a federal law known as the “Automobile Dealers’ Day In Court Act.” That legislation is an anomaly which allows dealers (franchisees) to sue in their home federal district court and recover legal fees if a manufacturer fails to “act in good faith in performing or complying with any of the terms or provisions of the franchise, or in terminating, canceling or not renewing the franchise with said dealer.” (These sorts of lawsuits would otherwise require a minimum of $75,000 at stake, would be governed by state law and would not have the threat of fee-shifting.)
Continue reading Want A Tesla? You Can’t Buy One Here.
The week before last I participated in a conference on mobile payment technologies. I expected to find out more about Square and other startups that have begun to revolutionize credit card acceptance by solo businesses like food trucks. What I learned instead is that this nascent industry is way bigger than the emerging near-field communications (NFC) protocol Apple unexpectedly did not include in its new iPhone 5. More surprisingly, it seems the biggest attraction for inventors and investors isn’t the payment transactions themselves at all.
Some take-aways:
- A bunch of different technologies are competing at the standards/platform level for mobile payment processing. These include EMV, Isis and TSM, as well as NFC. A major driver in adoption is that new ventures are cutting deals with point-of-sale (POS) equipment vendors to integrate their protocols into the next software updates for these ubiquitous checkout devices. The biggest barrier to adoption is security and PCI compliance.
- Many of the largest U.S. retailers (7-Eleven, Walmart, Sears, Best Buy, etc.) have teamed up in a joint venture called MCX, which has yet to decide on a common approach to use of smartphones as payment devices. By virtue of their ubiquity, the MCX players may have the scale to make their selection of mobile payment technology an inflection point in this transformation.
- The advantage of mobile payments to retailers is not simply allowing consumers a convenient way to make purchases. Rather, it is the Holy Grail of demographic, time and location information allowing Location Based Marketing (LBM) in the “last three feet.” By capturing GPS-enabled location data, using wireless geofencing to engage in push/pull marketing interactions — think shopkick and the like (disclaimer: shopkick has been a client of mine) — and mining that data, mobile payment companies will know more about consumer preferences and behavior than SKU-level retailers or the major credit card processors like Visa and MasterCard.
This presents some interesting questions from a business and social perspective. Will and should the same liability approach used for traditional credit cards, quite protective of the consumer, apply where the credit card is essentially integrated into a smartphone? How will mobile POS (MPOS) technologies change the retail experience, for instance use of swipeable tablets by sales clerks for “line-busting” at peak sales hours?  Will consumers be more comfortable with non-persistent technologies that utilize one-off QR codes for payment authentication than the always on NFC payment “wallet” backed by Google? Given the shambles of our national financial regulatory system in the U.S. post-2008, which of the slew of federal agencies, from the Federal Reserve to the much-maligned CFPB, will have jurisdiction to regulate this new market, and what sort of regulation is appropriate? Will consumers be more comfortable with non-persistent technologies that utilize one-off QR codes for payment authentication than the always on NFC payment “wallet” backed by Google? Given the shambles of our national financial regulatory system in the U.S. post-2008, which of the slew of federal agencies, from the Federal Reserve to the much-maligned CFPB, will have jurisdiction to regulate this new market, and what sort of regulation is appropriate?
Several months ago I asked, only partially in jest, whether technology had finally made currency irrelevant. Mobile payment technologies are only in their infancy in America, which lags well behind Japan and the EU. But in light of the scale of the U.S. economy, what the markets do here can have a profound effect on financial practices worldwide. The problem is that because the American approach to data privacy and ownership — where the manufacturer or merchant owns the transactional records — is so different, the driver of MPOS innovation here may not translate well abroad. Jerry Maguire’s catch phrase must be refined a bit, because mobile payment innovation in the U.S. wants to be shown the data, not the money.
Note: Originally prepared for and reposted with permission of the Disruptive Competition Project.


With calls for elimination of the U.S. penny going back decades, we are now on the verge of an inflection point for commercial payments. Between debit cards and emerging mobile payment systems, it seems innovation can disrupt even established roles of government that date to the U.S. Constitution (1789) and centuries beforehand.
Cash moved one small step nearer to its deathbed with the announcement on Wednesday that Square, the mobile payments start-up, would partner with Starbucks Coffee Company, reports Claire Cain Miller on Wednesday in The New York Times.
Daily Report: A Step Forward for the Mobile Wallet.
Social security checks are today almost completely a thing of the past. How many more years or decades before currency itself becomes extinct? And will this sea of change also disintermediate banks? Wait and see, but likely not for long.
Note: Originally prepared for and reposted with permission of the Disruptive Competition Project.

One year ago, the Wall Street Journal and other business publications reported that the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) had launched an investigation into “Twitter and the way it deals with the companies building applications and services for its platform.” The gist of the apparent competitive concern was that Twitter — which has grown from nothing to a significant new medium of social communications in just five years — had decided to limit access to its application programming interfaces (APIs) for third-parties, such as HootSuite, Echofon and the like, selling Twitter “client” software.
There’s no doubt Twitter is a disruptive technology. Of course, in 2000 the FTC was so convinced that an AOL-Time Warner combination would monopolize Internet content that it saddled the then-biggest merger with an onerous consent decree that evaporated, as did AOL itself, in the relative blink of an eye. Now it appears the agency is making the same mistake again. Assuming that a new and evolving technology represents a stand-alone market for antitrust purpose is dangerous where disruptive entrants are concerned, because as AOL illustrates, despite a first-mover advantage, even in network effects markets that may “tip” to a single firm competitive reality changes more quickly and in ways even the brightest pundits and government policy makers could never predict.
 Given that Twitter is in competition with Facebook, LinkedIn, Tumblr, Pinterest, Instgram and many other social networking and messaging services, including the near-moribund Google+, you’ve got to wonder why the FTC could even plausibly hypothesize that Twitter has anything approaching monopoly power. One can perhaps understand policy neophytes like Mike Arrington naively saying that Twitter has a “microblogging monopoly,” but not seasoned antitrusters. Given that Twitter is in competition with Facebook, LinkedIn, Tumblr, Pinterest, Instgram and many other social networking and messaging services, including the near-moribund Google+, you’ve got to wonder why the FTC could even plausibly hypothesize that Twitter has anything approaching monopoly power. One can perhaps understand policy neophytes like Mike Arrington naively saying that Twitter has a “microblogging monopoly,” but not seasoned antitrusters.
Twitter management explained at the time that “Twitter is a network, and its network effects are driven by users seeing and contributing to the network’s conversations. We need to ensure users can interact with Twitter the same way everywhere.” That’s a quintessential business judgment by corporate managers who presumably know their users (tweeters) and customers (advertisers) best. The company’s motivation is also clear and perfectly valid: it doesn’t want third parties making money — namely, coming into direct rivalry by selling ads — off its service, and thus depriving Twitter of potential revenue. It is incontestable that Twitter could vertically integrate into the client software business itself (a first step in which it did by acquiring TweetDeck), without any possible antitrust constraints. In this light, what could conceivably be wrong with Twitter setting ground rules that require third-party providers to utilize a common user interface (UI) scheme?
As Adam Thierer of the Technology Liberation front observed in 2011:
This episode again reflects the short-term, static snapshot thinking we all too often see at work in debates over media and technology policy. That is, many cyber-worrywarts are prone to taking snapshots of market activity and suggesting that temporary patterns are permanent disasters requiring immediate correction. Of course, a more dynamic view of progress and competition holds that “market failures” and “code failures” are ultimately better addressed by voluntary, spontaneous, bottom-up responses than by coercive, top-down approaches
Ironically, the Twitter decision to control API usage and effectively boot off some third-party software had only one economic effect. It cannibalized Twitter’s own developer and partner ecosystem, on which the company had relied heavily through its first years of extraordinarily rapid growth, in favor of an internal solution. That decision alienated some Twitter users and almost certainly reduced the absolute number of tweets sent and received — and thus the page views on which Twitter’s advertising rates are necessarily based. It also risked alienating the venture capitalists who have invested an estimated $475 million over just one-half of a year in companies working to develop Twitter-compatible apps and utilities. So the only firm Twitter is really hurting by this practice is Twitter itself. Eating your own ecosystem is hardly the stuff of monopolization.
Sacrificing independent distribution in favor of vertical integration is also a business model companies adopt and reject like roller coasters. In the oil industry, for instance, the most famous government antitrust case of them all is 1911’s Standard Oil, which broke up the vertically integrated petroleum monopoly assembled by John D. Rockefeller. Today, Standard’s offspring are rapidly disintegrating, divesting both wholesale distribution of refined oil products and retail gasoline dealerships. Sometimes conventional business wisdom extols vertical integration, other times it emphasizes an Adam Smith-type comparative advantage. But isn’t that the essence of marketplace competition? And in turn isn’t that something our nation’s competition policy should leave in the hands of market participants rather than government agencies?
The answer from Forbes is a simple yes:
If the FTC is indeed investigating Twitter, they are likely to find this case pretty boring. In acquiring the third party apps widely adopted by its users, Twitter is simply making a gradual, not to mention inevitable, move closer to its customer base. The startup is often slammed for its struggle to adopt a serious business model. Now that Twitter has finally figured out it is awfully difficult to build a business as a plumbing conduit, suddenly it’s lambasted as the next Microsoft.
In fact, the issue here is far more significant for technologies down the road that no one has as yet even conceived. Twitter seems sufficiently well-established that it will likely survive an FTC investigation, at least in the short run, and however misguided the government’s underlying assumptions may be. But start-ups which have not yet escaped from private betas and coders’ college dorm rooms will give pause, as they grow, before deciding to sever relations with partners  that helped them “get big fast.” The fear is that cutting off downstream firms, even if taken for objectively valid business reasons, will catalyze an FTC or European Union antitrust investigation of whether the firm has “abused” its “market dominance.” that helped them “get big fast.” The fear is that cutting off downstream firms, even if taken for objectively valid business reasons, will catalyze an FTC or European Union antitrust investigation of whether the firm has “abused” its “market dominance.”
A threat of government action can be just as debilitating to innovation as premature enforcement intervention into the marketplace. Let’s hope the FTC’s 2011 Twitter investigation is mothballed in 2012, and that in the future investigations of segment-leaders in nascent technology spaces are opened only where — unlike the case of Twitter — there’s clearly an economically valid market and practices involved which are unambiguously anticompetitive. The FTC has said nothing about the Twitter issue for a year, while the San Francisco Examiner revealingly comments that “[i]n the space of [that] year, the FTC has racked up more legal action involving the high tech world than the FCC and both houses of Congress combined.” Note to Chairman Leibowitz: it’s time to let this one go, now. If your agency wants to do that quietly in order to save face, no one in Silicon Valley will mind at all. We won’t tell.
Note: Originally prepared for and reposted with permission of the Disruptive Competition Project.
|
|










